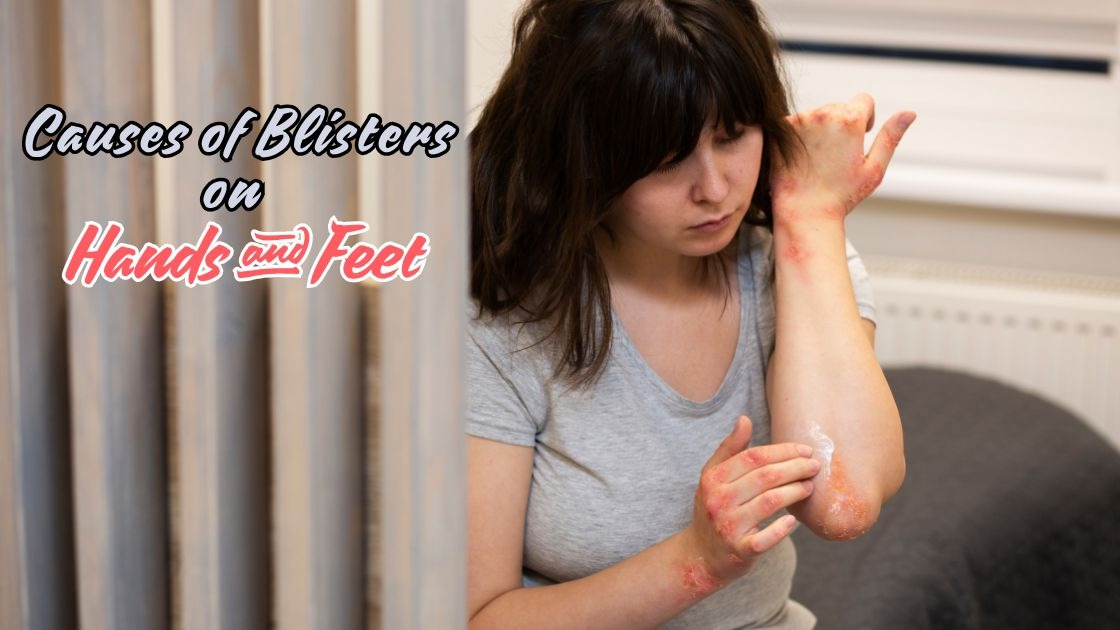
The cause of redness in inflammation is something many people notice but few truly understand. That warm, flushed skin around an injury or infection is actually your body’s brilliant defense system working hard to protect you. When tissues become damaged or irritated, your immune system triggers powerful responses that dramatically increase blood flow to the affected area. This surge brings essential white blood cells and healing nutrients exactly where they’re needed most.
Understanding this inflammatory response helps you distinguish normal healing from potential complications requiring medical attention. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the biological mechanisms behind inflammatory redness, common triggers, and what your body communicates through these visible changes. Whether you’re dealing with minor injuries or chronic conditions, this knowledge empowers smarter health decisions.

Understanding the Biological Process Behind Inflammatory Redness
The cause of redness in inflammation involves a fascinating chain of biological events. When your body detects tissue damage or harmful invaders, it immediately activates its defense mechanisms.
Your immune system releases chemical signals that trigger significant changes in nearby blood vessels. These vessels expand through a process called vasodilation, allowing more blood to rush toward the affected area.
This increased blood flow creates the characteristic red appearance we associate with inflammation. The redness serves as visual evidence that your body is actively working to repair and protect itself.
How Blood Vessels Respond to Injury
When cells become damaged, they release chemical messengers including histamine and prostaglandins. These substances communicate directly with blood vessel walls.
The vessels respond by relaxing and widening significantly. This expansion allows greater blood volume to pass through previously narrow passages.
Additionally, vessel walls become more permeable. This allows white blood cells and healing proteins to exit the bloodstream and enter damaged tissues directly.
The Role of Chemical Mediators in Inflammation
Understanding the cause of redness in inflammation requires examining the chemical signals involved. Your body uses several key messengers to orchestrate the inflammatory response.
Key Inflammatory Chemicals
- Histamine releases from mast cells within seconds of injury detection and causes immediate vessel dilation
- Cytokines coordinate communication between immune cells and sustain the inflammatory process
- Prostaglandins amplify inflammation signals and contribute to pain sensitivity
- Bradykinin increases vessel permeability and enhances the redness effect
These chemicals work together in a coordinated effort. Each plays a specific role in ensuring adequate blood circulation reaches the injury site.
Why Redness Matters in the Healing Process
The cause of redness in inflammation directly connects to your body’s healing process. This visible sign indicates several important functions occurring simultaneously.
Benefits of Increased Blood Flow
Redness signals that essential resources are arriving at the injury location. Your blood carries oxygen, nutrients, and antibodies necessary for tissue repair.
Immune cells travel through expanded vessels to fight potential infections. Without this response, even minor wounds could become life threatening.
The warmth accompanying redness also helps create an environment hostile to harmful bacteria. Elevated temperatures can slow pathogen growth while accelerating cellular repair activities.
Types of Inflammation and Their Characteristics
Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation appears rapidly after injury or infection. The cause of redness in inflammation during acute phases typically resolves within days or weeks.
Common triggers include:
- Cuts and scrapes
- Bacterial infections
- Burns and sunburns
- Allergic reactions
- Insect bites
This type represents your body’s healthy, protective response. The redness fades as healing progresses and threats are eliminated.
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation persists for months or even years. The cause of redness in inflammation in chronic conditions often involves ongoing immune system activation without clear resolution.
Conditions associated with chronic inflammation include arthritis, autoimmune disorders, and persistent infections. Managing these requires professional medical guidance.
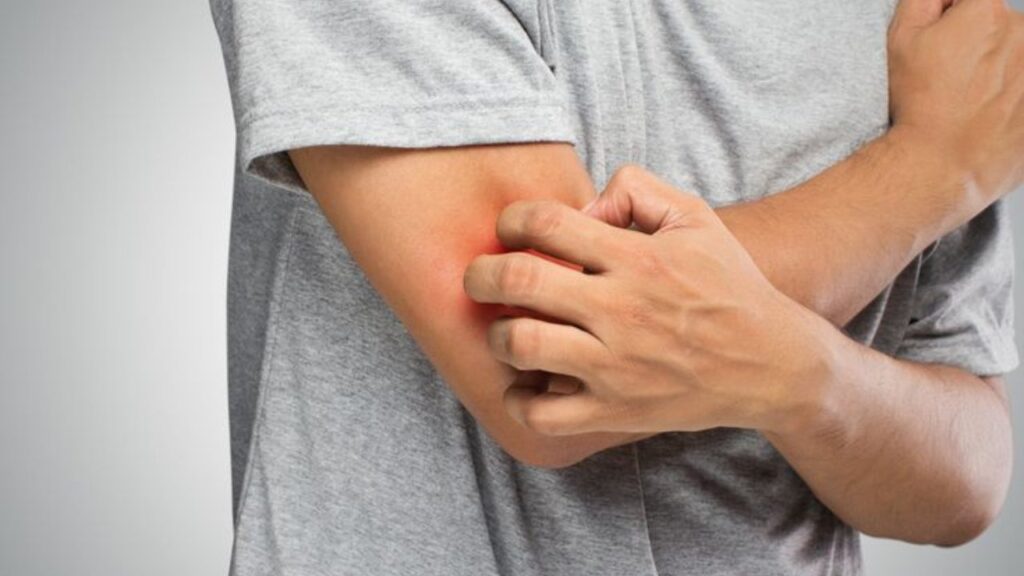
Common Triggers That Cause Inflammatory Redness
Understanding what activates the cause of redness in inflammation helps you identify potential health concerns early.
Physical Causes
- Mechanical injuries from accidents or exercise
- Temperature extremes including burns and frostbite
- Radiation exposure from sunlight or medical treatments
Biological Causes
Pathogens including bacteria, viruses, and fungi trigger strong inflammatory responses. Your immune system recognizes these invaders and initiates protective measures immediately.
Allergens can also cause significant redness. Substances like pollen, pet dander, and certain foods may activate inflammatory pathways in sensitive individuals.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While inflammation typically indicates healthy healing, certain signs warrant professional evaluation. Persistent redness lasting beyond two weeks may indicate underlying issues.
Spreading redness accompanied by fever could suggest serious infection requiring antibiotics. Similarly, inflammation without obvious cause deserves medical investigation.
Understanding the cause of redness in inflammation empowers you to distinguish normal healing from potential complications. Trust your instincts when something seems abnormal and consult healthcare providers when concerned.
Conclusion
Understanding the cause of redness in inflammation reveals how remarkably your body protects itself from harm. This visible response results from vasodilation and increased blood flow delivering essential immune cells and nutrients to damaged tissues.
Whether triggered by injuries, infections, or allergic reactions, inflammatory redness typically indicates healthy healing processes at work. Recognizing normal inflammation versus warning signs helps you make informed health decisions.
Remember that persistent or spreading redness may require medical attention. By understanding the cause of redness in inflammation, you’re better equipped to monitor your body’s responses and support its natural recovery mechanisms effectively.